Other Navigated rTMS applications
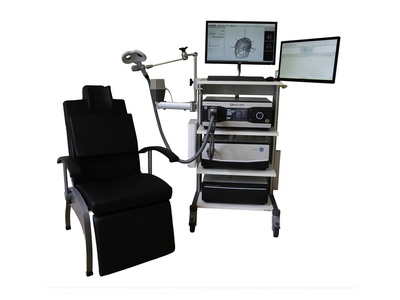
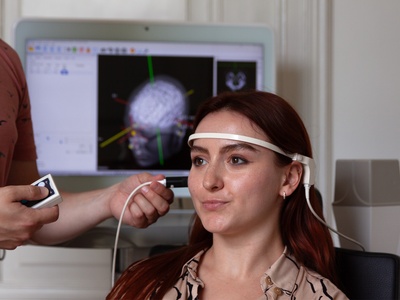
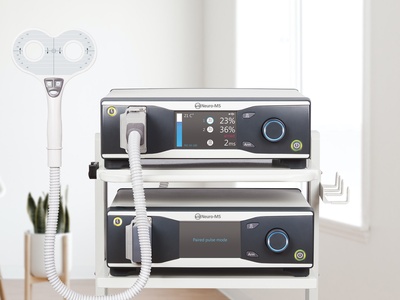
Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (rTMS) is a non-invasive brain stimulation technique which uses magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells. In patients with neuropathic pain rTMS treatments can be used for analgesic effects. Pain relief during rTMS therapies has been shown in patients suffering from neuropathic pain and resistant to pharmacotherapy for e.g fibromyalgia, orofacial pain, malignant neuropathic pain, central nervous pain. Adding MRI-guided neuronavigation to a TMS setup can improve the clinical outcome due to more accurate localisation of the target brain area. For different neuropathic pain types, the affected brain area seems to be different. Our navigation system with motor mapping can be used upfront in diagnosis of the affected area. We offer rTMS machines and MRI guided neuronavigation (Neural Navigator) separately as well as a complete solution (package) for research and clinical treatment. Specific diagnostic TMS and neuronavigation with motor mapping are also available. The complete solutions are CE certified for medical use in the EU and FDA cleared for clinical use in the USA.
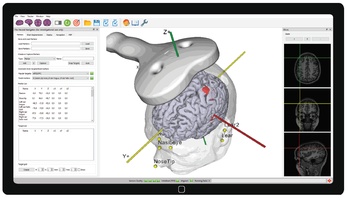
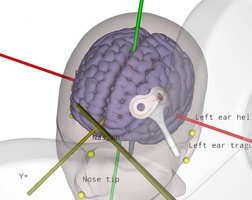
Reproducible coil placement using MNI
The neural navigator supports accurate reproduction of TMS coil positions using an MNI template. Similar to the standard navigation procedure, facial landmarks of the MNI template are captured on the participant's head. Next, the neural navigator adjusts the MNI template based on the geometry of the participant's head. MNI targets, …
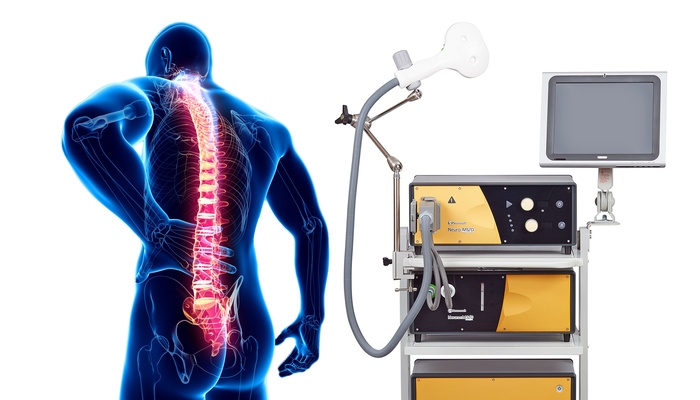
rTMS treatment of neuropathic pain
Neuropathic pain is characterized by a distinct set of symptoms, such as a burning sensation and pain resulting from non-painful stimulations. Fibromyalgia, orofacial pain, and phantom pain are different types of neuropathic pain. Neuropathic pain is caused by damage to, or a disease of the somatosensory system and it’s estimated …
Added value of MRI-guided neuronavigation
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) requires accurate placement of the TMS coil over the targeted brain area. Conventional placement methods in TMS are based merely on external landmarks of the head (5 cm rule, 10-20 EEG). This leads to inaccuracies in targeting of this brain area and herewith to suboptimal results …